1. What is Bamboo CI Server
Bamboo is a CI server which can be used to automate the release management to create a CD pipeline.
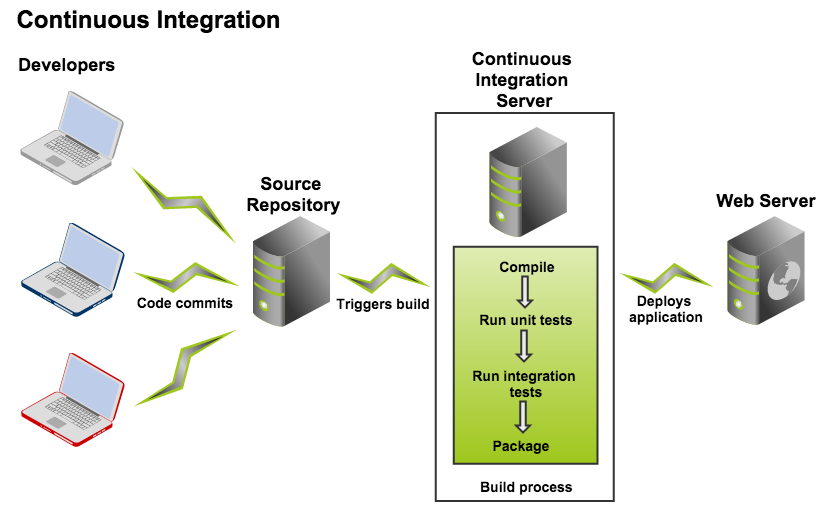
CI is a methodology in which a build, unit tests and integration tests are automatically triggered, whenever code is committed to the repository, to integrate new changes into the existing code base. As a result, it provides early ‘fail fast’ feedback on the quality of new changes.
Release management describes the steps that are typically performed to release a software application, including building and functional testing, tagging releases, assigning versions, and deploying and activating the new version in production.
2. What problems do Bamboo solve?
- An automated, reliable, build and test process
- Manage builds that have different requirements or targets
- Automatic deployment to a server, such as the App Store or Google Play
- Build and test processes are not dependent on a specific local environment.
- Builds and integration tests are triggered automatically as soon as new code is commited
- Optimize build performance through parallelism
- Leverage elastic resources
- Deploy continuously, for example to user acceptance testing (UAT).
- Implement release management
3. How does Bamboo do this?
- Bamboo is the central management server which schedules and coordinates all work
- Bamboo itself has interfaces and plugins for lots of types of work
- Bamboo first gets your source from a source repository, then it starts the build such as using Maven to call compiler
- Once project is built, you have “artifacts” (build results, e.g. an executable app, config files, etc.).
- Additional things can be done with the build artifacts:
- zip them up into a ZIP file and copy them somewhere
- run an install builder on them and create an MSI
- install them on a test server to make sure everything installs just fine
- Bamboo provides a web front-end for configuration and for reporting the status of builds
4. What does Bamboo need?
- A code repository that contains the complete source code for the project.
- Build scripts
- Test suites
5. How is a Bamboo workflow organized?
Project:
- Has none, one, or more, plans
- Provides reporting (using the wallboard, for example) across all plans in the project
- Provides links to other applications
- Allows setting up permissions for all the plans it contains
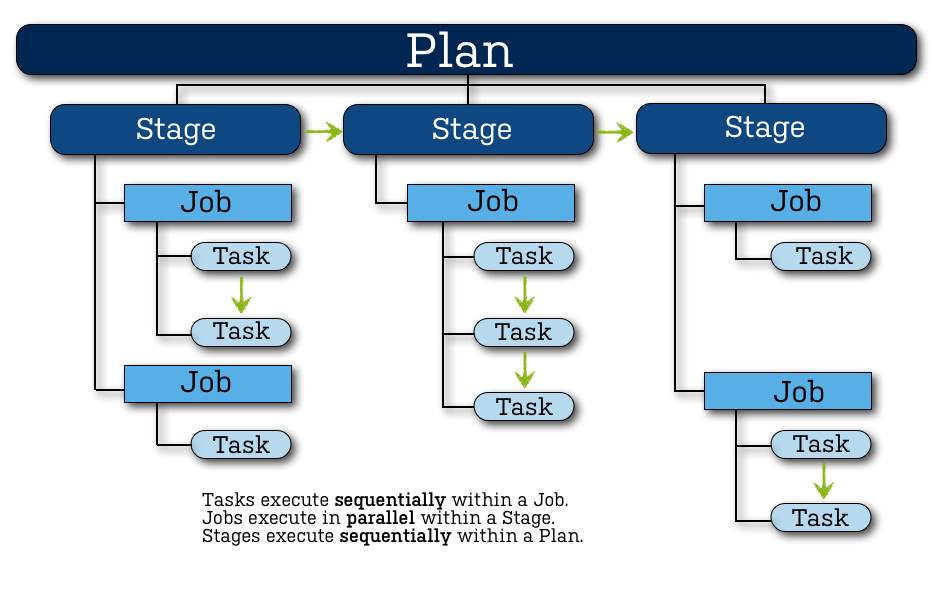
Plan:
- Has a single stage, by default, but can be used to group jobs into multiple stages
- Processes a series of one or more stages that are run sequentially using the same repository
- Specifies the default repository
- Specifies how the build is triggered, and the triggering dependencies between the plan and other plans in the project
- Specifies notifications of build results
- Specifies who has permission to view and configure the plan and its jobs
- Provides for the definition of plan variables
Stage:
- Has a single job, by default, but can be used to group multiple jobs
- Processes its jobs in parallel, on multiple agents (where available)
- Must successfully complete all its jobs before the next stage in the plan can be processed
- May produce artifacts that can be made available for use by a subsequent stage
Job:
- Processes a series of one or more tasks that are run sequentially on the same agent
- Controls the order in which tasks are performed
- Collects the requirements of individual tasks in the job, so that these requirements can be matched with agent capabilities
- Defines the artifacts that the build will produce
- Can only use artifacts produced in a previous stage
- Specifies any labels with which the build result or build artifacts will be tagged
Task:
- Is a small discrete unit of work, such as source code checkout, executing a Maven goal, running a script, or parsing test results
- Is run sequentially within a job on a Bamboo working directory
-
Previous
Continuous Integration vs. Continuous Delivery vs. Continuous Deployment -
Next
How Git Works?