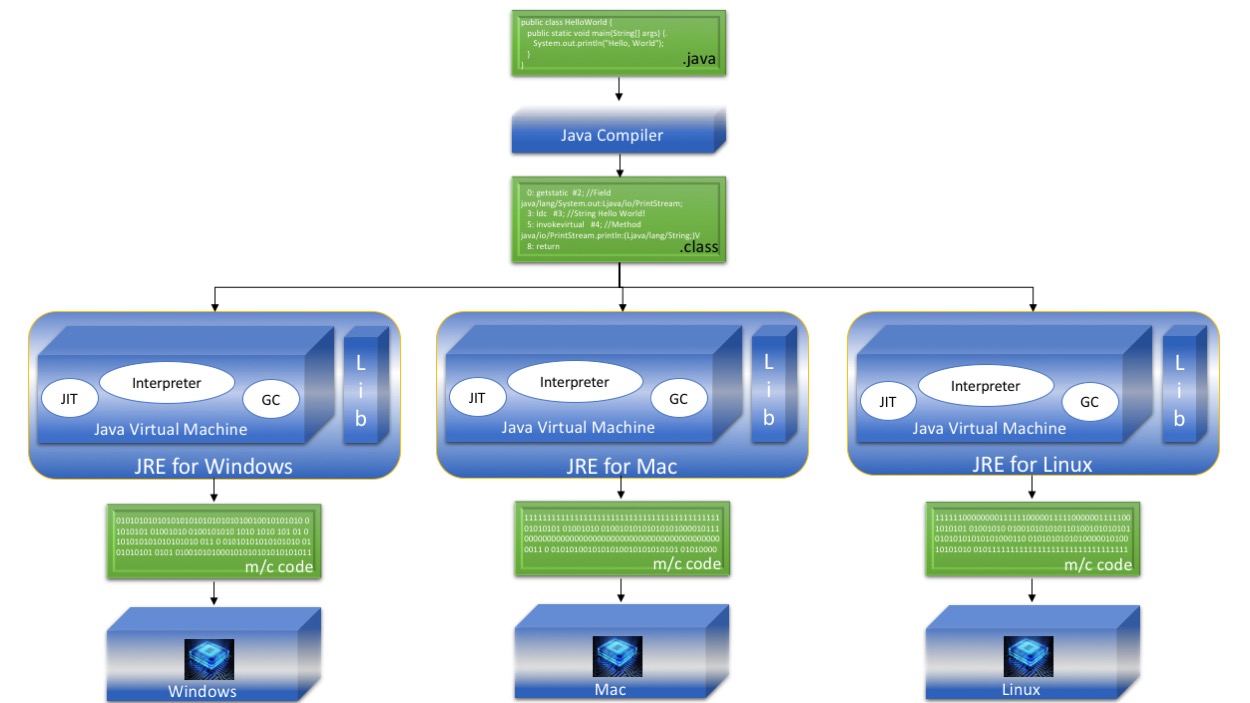
1. Java
1.1 Java Runtime Environment
Java needs a runtime environment called JRE for running a Java program. The JRE has a virtual machine called Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The JVM has many components like Garbage Collector(GC), Just-In-Time(JIT) compiler, Interpreter, Class Loader, Thread Manager, Exception Handler for performing different tasks at different times.
In addition to JVM, the JRE has set of libraries (e.g., rt.jar) to help a Java program at runtime. We have separate JREs for different platforms like Windows, Macintosh, and Linux and hence the JVM.
The source code (.java), which is compiled by the Java Compiler into an intermediate code called Bytecode (.class). This Bytecode is given to the JVM for execution on a given target platform. The JVM converts the Bytecode into machine code specific to the target platform before execution.
The execution of a Java program is explained in the picture below.
1.2 Java Web Application Architecture
The typical Java web application architecture has four layers: Client, Presentation, Service/Business, and Data.
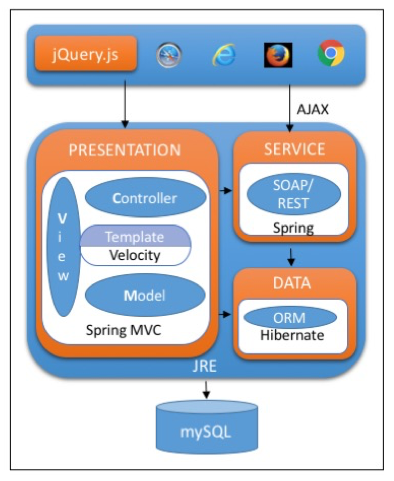
The Client layer may use libraries like jQuery for supporting AJAX functionality and for having some client-side validations and DOM manipulations.
The Presentation layer is the one that normally interacts with the Client layer. This layer would generally have implemented the MVC pattern for request and response handling. Frameworks like Spring MVC are used here. Also, there would be a template engine like Velocity to render the view dynamically based on a predefined layout.
The Service or Business layer is responsible for having business logic and communicates with the other layers. In the event of an AJAX request, this layer serves the data directly to the Client layer. This layer executes the business logic and responds back to the Presentation layer to update the model. The Service layer is the one that communicates with the Data layer to fetch or update required data. The service layer may have SOAP or REST service implementations using any framework, like Spring.
The Data layer normally uses some ORM frameworks, like Hiberate, or any JDBC-based libraries/templates (Spring JDBC Template) to communicate with any RDBMS, like Oracle.
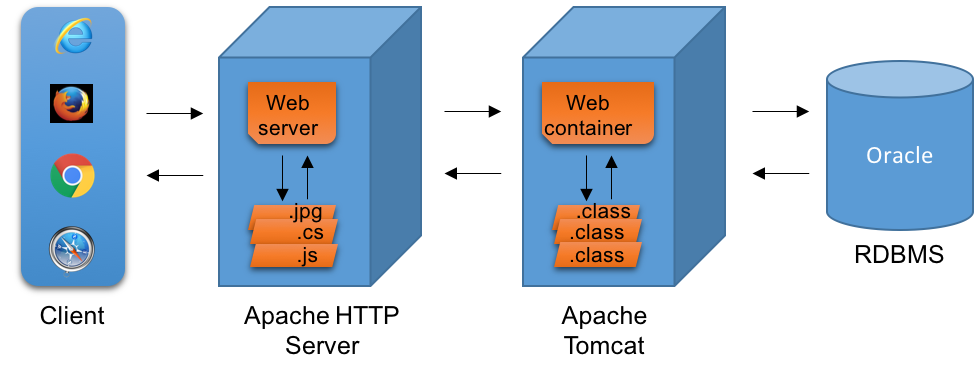
1.3 Java Deployment Architecture
The Java web application deployment architecture includes Apache HTTP server, which acts as a proxy server as well as serving static content. Dynamic content is served by a web container, which is actually an engine that processes the Java files.
The below diagram will explain the Java web application deployment architecture:
2. Node.js
Node.js is a runtime environment for running JavaScript-based applications.
2.1 Node.js Runtime Environment
Similar to JRE, the Node.js has a virtual machine called JavaScript Virtual Machine (JsVM?). It generates machine code for JavaScript-based applications to enable it on different platforms.
Node.js also has a set of libraries which may otherwise be known as Node API or Node Modules to help run JavaScript applications at runtime, similar to Java Libraries within the JRE. We have separate Node.js requirements for different platforms like Windows, Macintosh, and Linux and hence the JsVM.
The JavaScript Virtual Machine is nothing but the V8, the open source JavaScript engine from Google. Like the Java Virtual Machine, the JsVM (V8 engine) also has main components like JIT and GC for performing tasks, runtime compilation, and memory management respectively.
The source code is written in JavaScript (.js). There is no intermediate code generated before giving it to JsVM, the V8 engine. The JsVM takes this source code directly and compiles it to machine code specific to the given target platform for execution.
The above explanation can be understood easily in the below picture.
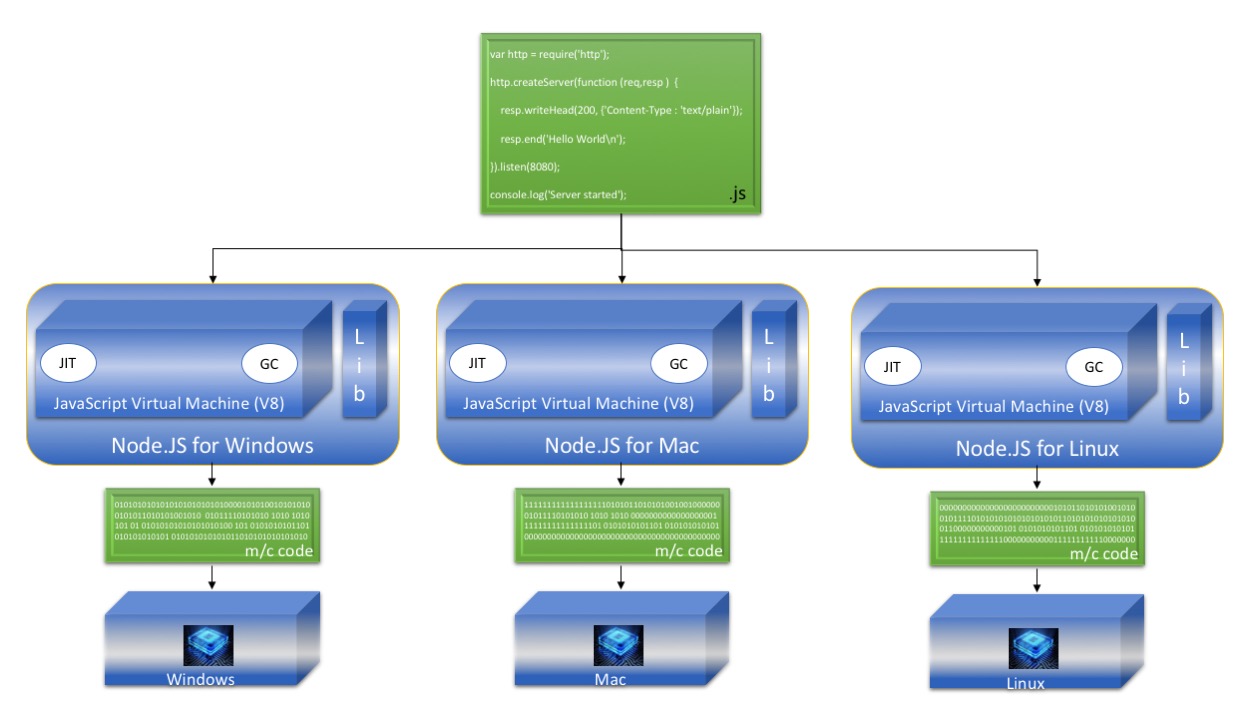
2.2 Node.js Web Application Architecture
A Node.js-based web application mostly follows the Java web application architecture. The main difference is in the client request processing. The client requests will be handled by a single thread, but asynchronously in the case of a Node.js application. With Java, each client request will be handled by a separate thread synchronously, and hence it is multi-threaded.
There are many frameworks/libraries available for Node.js-based web application development. The interesting point to note here is that all the frameworks/libraries are JavaScript based.
You can quickly understand the different layers and the framework/libraries used in those layers of Node.js application from the below picture.
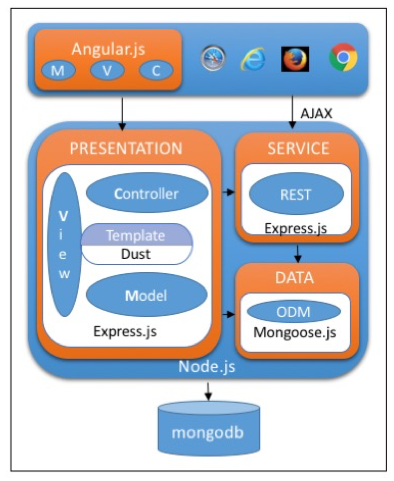
The Client layer uses Angular.js, a client-side MVC framework. The Presentation layer, as well as the Service layer, can be developed by using Express.js, a JavaScript-based web application framework. This also comes with a standalone server for running Node.js applications. The Data layer uses an Object Data Modelling module (e.g. Mongoose.js) for communicating with NoSQL databases like MongoDB.
This particular stack is called MEAN , which consists of MongoDB, Express.js, Angular.js, the client side MVC framework and Node.js, the runtime environment.
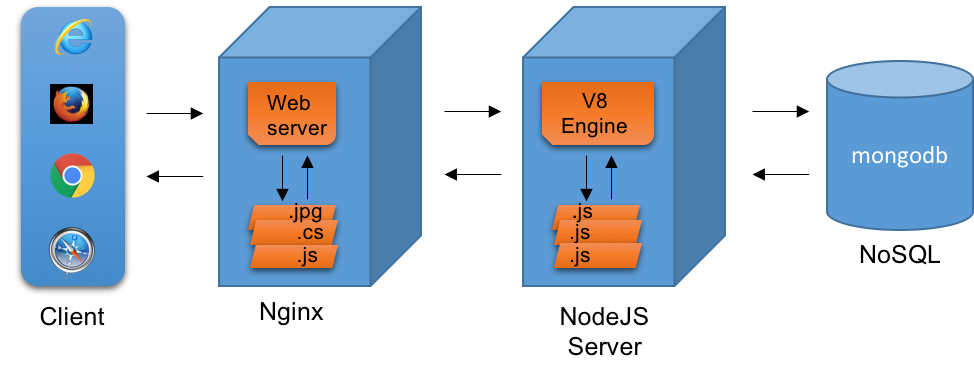
2.3 Node.js Deployment Architecture
Node.js-based web application deployment architecture follows Java’s web application deployment architecture. It has an NGINX server, which acts like an HTTP proxy server, as well as serves the static content. The dynamic content is served by a Node.js server, which contains an engine to process the JavaScript files.
Below is the diagram that explains the Node.js based web application’s deployment architecture.