Context
You have applied the Microservices architecture pattern and the Database per service pattern. As a result, it is no longer straightforward to implement queries that join data from multiple services. Also, if you have applied the Event sourcing pattern then the data is no longer easily queried.
Problem
How to implement a query that retrieves data from multiple services in a microservice architecture?
Solution
Define a view database, which is a read-only replica that is designed to support that query. The application keeps the replica up to data by subscribing to Domain events published by the service that own the data.
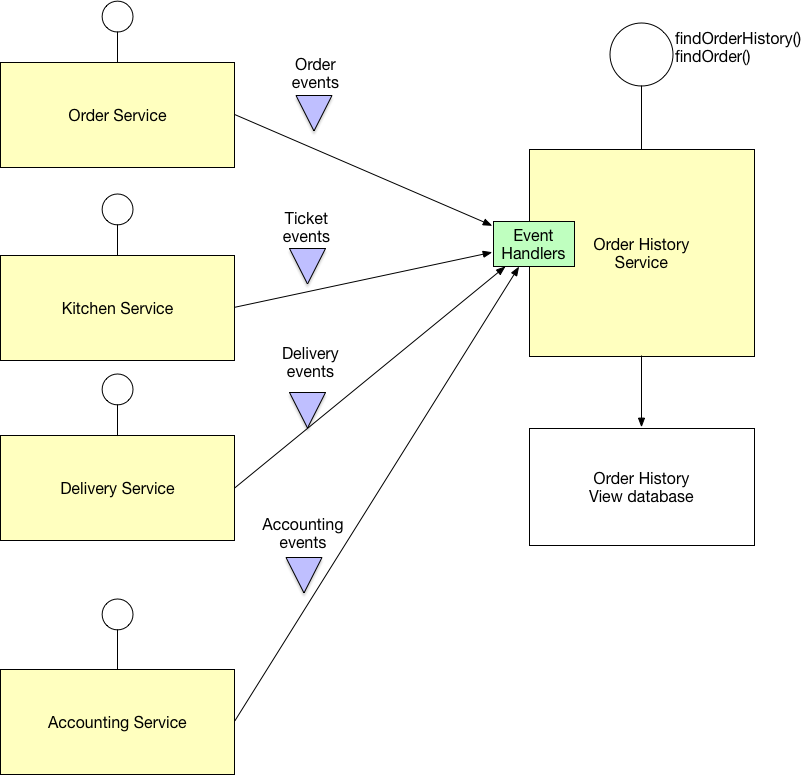
Examples
My book’s FTGO example application has the Order History Service, which implements this pattern.
There are several Eventuate-based example applications that illustrate how to use this pattern.
Resulting context
This pattern has the following benefits:
- Supports multiple denormalized views that are scalable and performant
- Improved separation of concerns = simpler command and query models
- Necessary in an event sourced architecture
This pattern has the following drawbacks:
- Increased complexity
- Potential code duplication
- Replication lag/eventually consistent views
Related patterns
- The Database per Service pattern creates the need for this pattern
- The API Composition pattern is an alternative solution
- The Domain event pattern generates the events
- CQRS is often used with [Event sourcing]
See also
- Eventuate, which is a platform for developing transactional business applications.
- The book Microservices patterns describes this pattern in a lot more detail.